1. What is an AC Induction Motor?
An AC induction motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy using alternating current (AC) and the principle of electromagnetic induction. Its most notable feature is that it does not require permanent magnets, brushes, or commutators, which are physical contact components. As a result, it has a simple structure, long lifespan, and low maintenance costs.
2. Working Principle
Currently, single-phase AC induction motors and three-phase AC induction motors are available on the market. Below is an explanation of their working principles:
Single-phase AC induction motors consist of a stator and a rotor. When the stator winding is connected to a single-phase AC power supply, it generates a pulsating magnetic field (not a rotating magnetic field). Since a single-phase current cannot directly form a rotating magnetic field, the motor requires additional devices (such as a starting capacitor or split-phase winding) to create a phase difference during startup, forming an equivalent rotating magnetic field. This magnetic field induces eddy currents in the rotor bars, and the interaction between the eddy currents and the magnetic field generates torque, causing the rotor to rotate. After startup, the centrifugal switch may disconnect the auxiliary winding, and the motor continues to operate solely on the main winding.
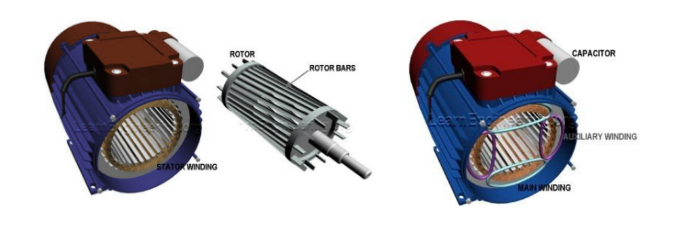
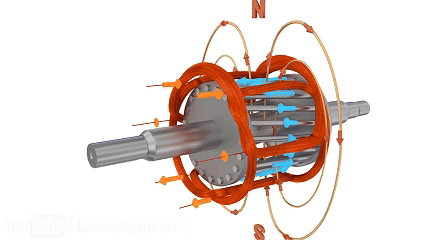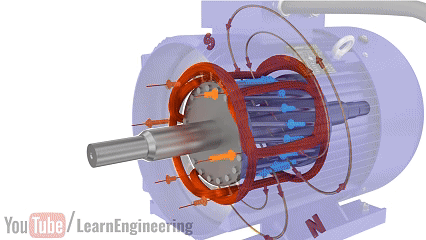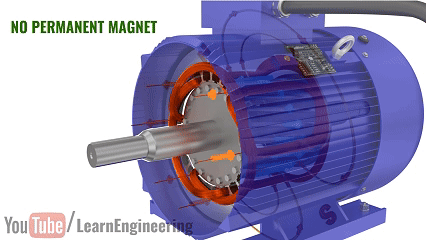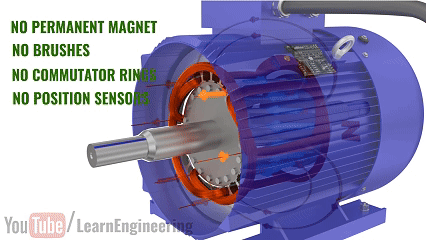
Three-phase AC induction motors have stator windings composed of three sets of spatially symmetrical coils (120° apart). When connected to a three-phase AC power supply, the phase difference of the three-phase currents synthesizes a continuously rotating magnetic field in the stator. The rotor is typically a squirrel-cage structure, and its bars induce currents when cut by the rotating magnetic field, forming a rotor magnetic field. The interaction between the stator and rotor magnetic fields generates electromagnetic torque, driving the rotor to follow the direction of the rotating magnetic field (at a speed slightly lower than the synchronous speed, known as "slip").
3. Product Features
AC induction motors have become the most widely used motor type globally, primarily due to the following advantages:
- Low cost: Made from common materials (iron, copper, aluminum) and mature manufacturing processes, resulting in low production costs.
- Robust and durable: No brush wear, suitable for harsh environments such as high temperatures and dust, with a long service life.
- Simple maintenance: Routine maintenance only requires checking bearings and lubrication, keeping maintenance costs low.
- Flexible speed control: When paired with a frequency converter, the speed can be easily adjusted to meet different load requirements.
Note: Single-phase motors generate a torque opposite to the direction of rotation during operation, so they cannot change direction in a short time. To change direction, ensure the motor has completely stopped before operating.
4. Application Scenarios
Single-phase motors have a simple structure and low cost but provide low starting torque, making them suitable for light-load applications such as household appliances (e.g., fans, washing machines).
Three-phase motors do not require additional starting devices and can self-start. They operate smoothly, with high efficiency and torque, making them widely used in industrial equipment (e.g., water pumps, compressors, machine tools).
| Application Scenarios | Examples |
|---|---|
| Household Appliances | Washing machines, electric fans, air conditioner compressors |
| Industrial Field | Water pumps, fans, conveyor belts, machine tools |
| Transportation | Electric vehicles (some models), auxiliary systems for high-speed trains |
| Renewable Energy | Pitch systems for wind turbines |
| Construction Equipment | Elevators, lifts, and heavy equipment at construction sites |
| Agricultural Machinery | Water pumps, automatic irrigation systems, and other agricultural equipment |
| Robotics | Driving robotic arms and other motion components |